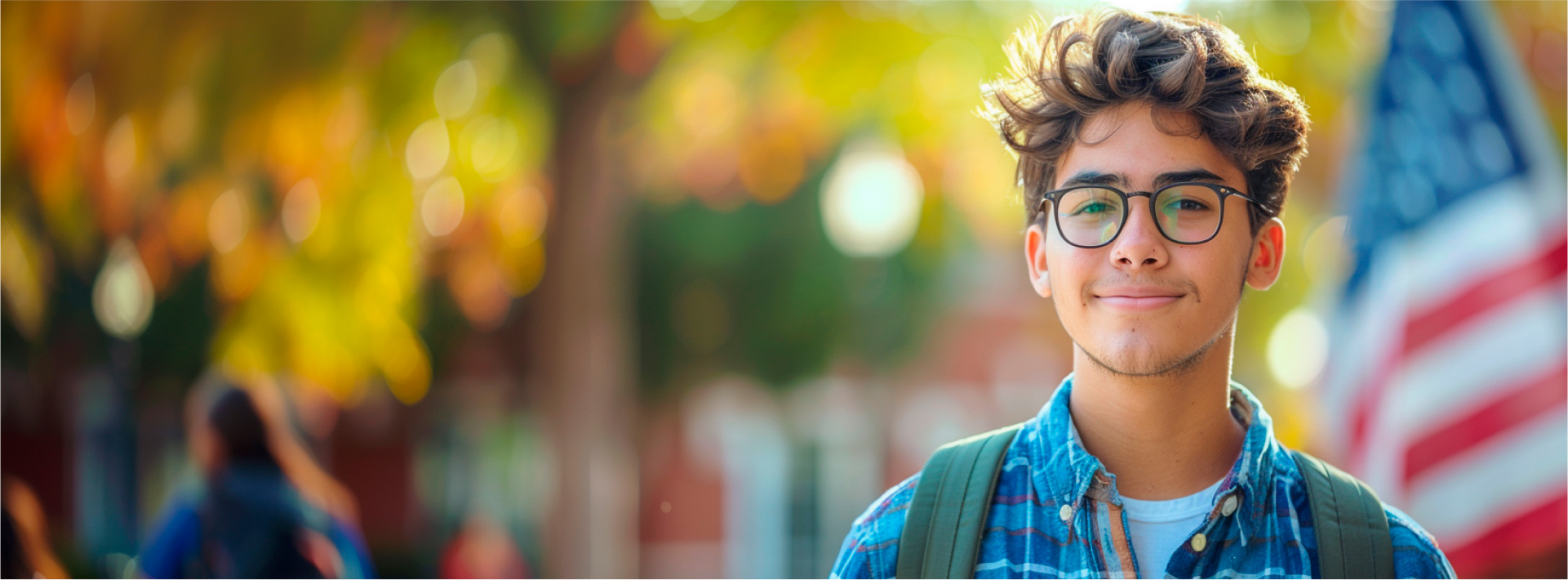


Bachelor’s Degree in Computer Science
Become an expert in computer science, a key professional in any industry. This degree equips you with comprehensive training, encompassing everything from fundamentals to the latest developments in a field that is constantly evolving.
Apply for a scholarship


Format 100% online

Start date May 2025
US Degree Accredited
Language English
Join the dynamic world of technology
Your study plan covers a wide range of subjects including programming, data structures, algorithms, databases, computer networks, software development, and system design. It also takes a deep dive into critical fields such as artificial intelligence, cybersecurity, data analysis, and cloud computing. All in all, you’ll learn everything you need to know to tackle real-world challenges in today’s job market.
With this degree program, you’ll have the opportunity to apply your theoretical knowledge in practical projects, engaging in active and collaborative learning with your peers.
When you finish your degree, you’ll be prepared to enter the workforce with a highly competitive profile, equipped with the skills to innovate and lead in the field of computer science.
What will you learn during your Bachelor’s in Computer Science?
Discover diverse areas of knowledge, starting with a solid foundation in mathematics and programming and the basic principles of coding and computational logic. Enjoy classes that teach you how to organize and manage information efficiently by designing and defining the appropriate data structures and managing the databases best suited to each practical situation. You will learn how to:
- Understand the characteristics, functionalities, and structure of distributed systems, computer networks, and the internet.
- Identify database functionalities and structures, along with the design, analysis, and implementation of applications based on databases.
- Use tools for storing, processing, and accessing information systems, including those that are web-based.
- Apply a variety of programming techniques.
- Identify the principles, methodologies, and life cycles of software engineering.
- Evaluate human-computer interfaces that enable accessibility and usability for computer systems, services, and applications.
- Determine the best cybersecurity options for designing systems to protect data and system infrastructure security.

Format
We offer this U.S. degree in an online learning format to give you maximum flexibility. Advance at your own pace, anytime and anywhere.
Online
Tuition
Per credit
Fees
Start date
May 2025
Language
English
Duration
4 years (12 semesters)
Application fee
- $50 (U.S. residents).
- $150 (international students).
Scholarships
See all the scholarships we have available for those who qualify, along with our no-interest payment plans. If you have any questions about your personal situation, we are here to help.
Career opportunities
AVERAGE SALARY
EMPLOYABILITY
Gain the necessary knowledge and skills to work in a wide range of industries, from automation and robotics to public and private companies dedicated to developing and managing computer and telematics systems. You will be an ideal candidate for organizations looking for a professional who is able to develop and utilize technologies as well as design, create, and manage data processing systems in a wide range of applications.
Your professional profile will align with the following areas of employment:
- Software and services: applications analyst and developer, software engineer, hardware engineer, programmer analyst, technology consultant, or systems architect.
- Products and systems: systems engineer, technician, or specialist.
- Telecommunication: software and network architect, data communications engineer, or software project manager.

Success stories

Melvin Vidal Rodríguez De la Cruz
Executive Manager
He manages consulting firms that deliver outsourced tax and HR services to 62 businesses in the Dominican Republic.

Ingla Damyanti Madho
HR Manager
She is responsible for recruitment, employee relations, performance management, and strategic HR planning to drive company success.

Ana Laura Chiban
Project Manager Specialist - Logistic Home Renovation
She is responsible for assigning tasks and communicating with project stakeholders to determine project requirements and objectives.

Carlos Wandy Martínez de Aza
Teacher
He works in a community of 1,800 students facing social and socioeconomic challenges, teaching Math, Spanish, Social Studies, and Natural Sciences for 8 hours a week.

Hipolito Enmanuel Nuñez Muñoz
Control Room Operator
He has 7 years of experience in monitoring and controlling a coal-fired power plant.

Christa Rose Marie Lewis
Graphic Designer - Ministry of Education and National Reconciliation of St. Vincent and the Grenadines.
She is in charge of developing visual designs and illustrations to support the promotion and production of curricular guides, manuals, assessment materials, and multimedia content.

Euler Caruajulca Colunche
HR Selection and Training Assistant
He is in charge of the employee selection process and helps train company personnel.

Stephanie Natasha Samsair
PhD student in Process Engineering
She studies the technical and managerial aspects of process engineering.
Program
120 Credits
At MIU, each academic term lasts 15 weeks, equivalent to one semester in the U.S. education system. We have three semesters each year: from January to May, from May to August, and from August to December.
See all the courses included in your degree program.
First year
1st semester
English Composition I
ENC1101
3 US Credits
English 1101 is a college-level writing course that introduces students to the various forms of academic discourse. This course focuses primarily on the basic elements of college composition and writing as a process in both narrative and analytical forms. Students will investigate the importance and promise of effective written communication in various personal and professional contexts and identify effective strategies through critical analysis of written works as well as their own writing. Finally, this course prepares students for more advanced research analysis by connecting students to important avenues of research.
Course Outcomes:
1) Identifies different academic writing styles. Students identify and apply different styles of academic writing, choosing the one that best fits their audience.
2) Communicates effectively based on research. Using a specific academic style, students demonstrate their ability to effectively communicate their ideas based on extensive analysis and research.
3) Influence others through effective communication. Students demonstrate their ability to influence with clear and effective communication strategies based on critical analysis and logic.
Sociology
SYG2001
3 US Credits
Students should understand their role in society and be capable of interpreting the social phenomena surrounding them. This course provides students with a basic understanding of how the society functions, and specifically how groups work.
Course Outcomes:
1) Student will be able to identify social facts and theories, explaining how they had an impact on the development of sociology.
2) Students will be able to apply empirical observation, recognizing the importance of social facts for strategic analysis of sociological circumstances.
Students will be able to define and explain main characteristics of social institutions around world and its impact on the development of policies for social change.
College Mathematics I
MAC1005
3 US Credits
This course provides a general introduction to college mathematics. Students learn the following mathematical concepts in a logical sequence that increases in difficulty as students gain command of a concept: polynomials, equations, inequalities, the straight line, Cartesian coordinates, functions and graphs, systems of linear equations, logarithms and exponentials, matrix algebra, limit of a function, and derivate of a function and integral.
Course Outcome:
Students will be able to apply mathematical concepts in a logical sequence that increases in difficulty as students gain command of basic algebra concepts, appreciating the importance of analytic and abstract thinking.
Advanced Writing Techniques
WRI100
3 US Credits
This course provides writing instruction for students in the Bachelor of Science. Students practice and reflect on writing in professional, public, and academic genres, such as technical reports, progress reports, proposals, instructions, presentations, and technical reviews, relevant to technical professions and individual student goals. Students evaluate a wide variety of sources and develop expertise in audience analysis, critical research, peer review as well as practical skills in writing more sophisticated text and essays.
Course Outcomes:
1) Students will be able to apply the main techniques and procedures of descriptive statistics and the inferential statistics techniques to specific situations in business and social sciences.
Students will learn how to solve statistical problems by hand and using computer software.
2nd semester
College Mathematics II
MAC1014
3 US Credits.
This course provides students with the methodologies required to understand the role played by the inductive method in this field of Mathematics. Trigonometric functions, identities and conditional equations, solution of triangles, trigonometric forms of complex numbers are all taught.
Prerequisite(s): MAC 1005
Course Outcomes:
1) Students will be able to use and apply the inductive method through different exercises, analyze the role played by it in this field of Mathematics.
2) Identify sequences and series.
3) Solve series, both numerical and of functions
4) Understand and solve the fundamental differential equations.
5) Evaluate differential equations of the first and second order.
6) Solve systems of differential equations
Apply the studied notions to the solution of problems and exercises.
General Psychology
PSY2001
3 US Credits.
This course places an emphasis on behavior and the factors that influence it, as well as on describing the cognitive, affective and personality factors that make up behavior. The knowledge acquired by the students in this course will provide them with a holistic view of man and serve as the basis for understanding other courses related to behavioral science.
Course Outcomes:
1) Students will be able to identify the psychological processes that shape personality and human behavior, recognizing the main theories of this field and analyze in a critical way the attitudes and conducts of the people in different environments.
2) Students will be able to relate biological and social processes that impact the development and expression of Human behavior, recognizing the importance of both nature and nurturing.
English Composition II
ENC1102
3 US Credits.
English 1102 focuses students on the importance of research to advancing knowledge for various purposes. This course will build on the foundations of composition and introduce students to the research process and the analysis and evaluation of various sources. Students will investigate the writing process for research as well as appropriate research methods and skills. Additionally, this course offers multiple opportunities to engage in the important tasks of revision and editing and will ask students to incorporate feedback to improve their writing.
Prerequisite(s): ENC 1101
Course Outcomes:
1) The student will be able to identify and elaborate personal writing through different expressions of literary forms.
Students will be able to structure a logic and analytical academic paper based on scientific research using the latest APA norms.
Speech
SPC1017
3 US Credits.
This course introduces students the necessary skills to become a better public speaker through theory and, most importantly, practice. Students will learn concepts, skills, and models of communication. Concepts include how to adapt a speech for different occasions and audiences, how to effectively support your ideas, how to select and organize materials in preparation for a speech, and how to utilize multimedia tools in presentations. This course is relevant in academic, business, and social settings in which the student will become a better public speaker and listener. Students will also be exposed to thinking about and maintaining ethical standards in public speaking.
Course Outcomes:
1) Students will be able to identify communication concepts that serve as a basis for effective speaking and apply this conceptual knowledge in practice to give effective and persuasive speeches.
2) Students will be able analyze and evaluate presentations made by others using the main components of technical and organizational areas in a speech.
Students will be able to develop and demonstrate verbal, nonverbal, and research competencies through researching, preparing, and delivering presentations relevant to your audiences, demonstrating confidence to speak publicly in a variety of situations.
3rd semester
Macroeconomics
ECO2013
3 US Credits.
This course explores the way the overall levels of output, income, employment and prices are determined in a capitalist economy. The focus is on the forces that act to shape these factors and determine their fluctuations. The role of government fiscal and monetary policy in influencing the level of economic activity is also a major area of study. The impact of international transactions on the domestic economy also is discussed.
Course Outcomes:
1) Students will be able to define and identify how the overall levels of output, income, employment, and prices are determined in a capitalist economy.
Students will be able to recognize and value how government polity, credit market, banks and national and foreign currency works and shapes the fluctuations in the economy of a country.
Microeconomics
ECO2023
3 US Credits.
This course examines the role of economic systems in allocating scarce resources to satisfy the needs and wants of individual members of a society. After a brief exposure to alternative economic systems, the focus becomes the nature and performance of American capitalism. Primary emphasis is placed upon the development of models that explain the behavior of consumers, producers and resource suppliers in various market structures.
Course Outcomes:
1) Students will be able to understand and identify development of models that explain the behavior of consumers, producers, and resource suppliers in various market structures.
2) Students, through the analysis of different companies competing in a market, will be able to discern strategic behavior in business decision-making.
Students will be able to understand and comprehend the application scope of the application of the Dynamic Game Theory to different economic and business scenarios.
World History
WHO1026
3 US Credits.
This course provides students with a general understanding of the changes that have taken place in the world since the appearance of humankind. This course covers the breakup of the Old World, the events of the Middle Ages in Europe, the rise of industrialization, the growth of imperialism, the two world wars, the changes in the post war world, and globalization. This course also introduces students to the economic, political, and social processes in the world of today.
Course Outcomes:
1) Students will be able to identify and relate notable events, development of political and economic and their influence on historical stages.
Students will be able to analyze how historical events and its development can be apply to current world events.
Statistics
STA2311
3 US Credits.
This is a fundamental course in the application of statistics. In this course, students will learn to apply statistical techniques to a variety of applications in business and the social sciences. Students will learn how to solve statistical problems by hand and with the use of computer software. Topics include probability distribution functions, sampling distributions, estimation, and hypothesis testing and linear regression.
Course Outcomes:
1) Students will be able to apply the main techniques and procedures of descriptive statistics and the inferential statistics techniques to specific situations in business and social sciences.
Students will learn how to solve statistical problems by hand and using computer software.
Second year
4th semester
Computer Programming
COP2210
3 US Credits
The course will train the student to work effectively as entry-level developers. The beginning students learn the fundamentals of computer programming using one specific object-oriented Programming language. Afterwards, students will learn the system development process. They will work on individual projects reflecting industry work scenarios.
Course Outcomes:
1) Students will be able to describe the system development process. They will work on individual projects reflecting industry work scenarios.
2) Students will be able to employ an object-oriented Programming language as entry-level developers. They will construct basic programs for solving practical problems.
Physics
PHY2048
3 US Credits
The aim of this course is to provide the necessary elements to understanding the laws of classical physics. The lessons are taught through videos about mechanics, thermodynamics, electromagnetism, and optics. The teaching provides a foundational knowledge necessary for engineering courses.
Course Outcomes:
1) Students will be able to interpret the laws of classical physics. They will discuss about mechanics, thermodynamics, electromagnetism, and optics.
2) Students will be able to identify the classical physics foundational knowledge necessary for engineering courses.
Computer Architecture and System Software
EEL3768
3 US Credits
Two different parts, “Electronic calculators” and “Operating Systems” compose the course. The main objectives of the first part are: understanding the structure of modern electronic calculators, analyzing its main components, adopting the classical chart of “level hierarchy”. An in-depth dissertation on logical-digital levels, on microarchitecture, on instruction sets on operating systems, and set up language will be held. Some study cases will also be proposed, especially those, which use common-use architecture, as Intel Pentium 4, Sun Ultra-SPARC III, and Intel 8051 (used in embedded systems). There will also be given tips on modern electronic calculators’ virtualization ability, together with examples of their usage, stabilizing server factory. For what concerns the second part, the main objective is offering specific competences on the structure of a modern operating system, enriching them with details regarding Unix operating system (with references to Linux operating system), and giving methodology knowledge which are used to solve typical issues on resources management in a modern operating system. The topics discussed will also include Thread and Processes, deadlock, memory management, swapping, virtual memory, Input/Output, Users graphic interfaces, web terminal. On a practical level, it will offer system programming notions (called “of the system”, usage of tools such as compilers, linker, etc.), and rival programming, together with basic notions on system usage, Unix-compliant (the operating system used will be Unix).
Course Outcomes:
1) Students will be able to evaluate the structure of modern electronic calculators, analyzing its main components, adopting the classical chart of “level hierarchy”.
2) Students will be able to examine modern electronic calculators´ virtualization ability, together with examples of their usage, stabilizing server factory.
3) Students will be able to assess the structure of a modern operating system, enriching them with details regarding Unix operating system.
5th semester
Operating Systems
COP2300
3 US Credits
The main objective of this course is to offer a general study of operating systems. The evolution that these have had over time will be analyzed, as well as their general structure. Designing an operating system is associated with control over what, who and how computer systems can be used, which have become a fundamental part of today’s economy, industry, and society. The student must know the basic concepts necessary to understand how operating systems are designed and implemented. In order to get this goal, the course is structured in the following basic blocks: structuring and designing of operating systems, concurrency, and memory management. Therefore, the course will define the main areas of operating systems, as well as their main functions. The tools that allow knowing an operating system will be studied to facilitate the work of users and administrators. In addition, it will introduce concurrent programming, highlighting its advantages and problems to synchronize processes, and defining techniques to communicate processes and other techniques to synchronize them avoiding deadlocks. Finally, as the main foundation of the software, the efficient use of memory will be analyzed, and the concept of virtual memory will be introduced.
Course Outcomes:
1) Students will be able to explain the evolution and general structure of Operating Systems.
2) Students will be able to interpret how operating systems are designed and implemented.
3) Students will be able to recognize the efficient use of memory and the concept of virtual memory.
Information System and Safety
ISM4300
3 US Credits
The course wishes to supply the student with the knowledge to understand the different aspects in which the subject of computer system safety branches out. A lot of technical aspects will be discussed, especially relating to cryptographic, to system safety, and to networks safety, System safety will be studied also from a legal and management point of view.
Course Outcomes:
1) Students will be able to revise technical aspects related to cryptographic, system safety, and to networks safety.
2) Students will be able to distinguish system safety from legal and management point of view.
Human-Computer Interaction
CEN2710
3 US Credits
The main objective of this course is to study the relationships that are established between people and electronic devices, such as computers, tablets or mobiles. There is no doubt that these have become an essential part of our lives. Personal relationships, work, information and social networks are permeated with the use of these devices, so they are used in many different moments a day. Therefore, the main questions to be analyzed are: how is the interaction between people and these devices established, how can we act as computer engineers to facilitate and optimize such relationships. To answer these questions, the interaction between the person and those devices, especially the computer, will be studied from a multi and interdisciplinary perspective. It will be done by adopting sociological, psychological, cognitive and ethical points of view, on one hand, and working from the engineering and design, on the other. Emphasis will be placed on people with functional diversity, who are especially sensitive to accessibility, usability and design issues. In addition, the course Will analyze the challenges that the interaction between the person and electronic devices is facing now and in the future.
Course Outcomes:
1) Students will be able to analyze the relationships that are established between people and electronic devices, such as computers, tablets, or mobiles.
2) Students will be able to examine, adopting sociological, psychological, cognitive, and ethical points of view, the relationships between people and electronic devices. Emphasis will be placed on people with functional diversity, who are especially sensitive to accessibility, usability, and design issues.
Fundamentals of Software Engineering
CEN4072
3 US Credits
Software engineering is the branch of computer science that creates practical, cost-effective solutions to computing and information processing problems, preferentially by applying scientific knowledge, developing software systems in the service of mankind. This course covers the fundamentals of software engineering, including understanding system requirements, finding appropriate engineering compromises, effective methods of design, coding, and testing, team software development, and the application of engineering tools. The course will combine a strong technical focus with a capstone project providing the opportunity to practice engineering knowledge, skills, and practices in a realistic development setting with a real client.
Course Outcomes:
1) Students will be able to compare cost-effective solutions to computing and information processing problems, preferentially by applying scientific knowledge, developing software systems in the service of humanity.
2) Students will be able to value system requirements, finding appropriate engineering compromises, effective methods of design, coding, and testing, team software development, and the application of engineering tools. The course will have a capstone project.
6th semester
Web Application Development
COP3874
3 US Credits
The main objective of this course is to study the development of distributed Web applications. The fundamental concepts to understand the architecture of a distributed application will be presented. For this, it will be necessary to know the particular aspects of the client-server architecture. Aspects such as the most used programming languages in this type of architecture will be also covered, differentiating between server languages and client languages. Since the computational cost is increasing, aspects related to the Grid architecture and Web services will be studied. The course is organized into the following areas: introduction to Web applications where the http protocol is analyzed, component-oriented programming, and Web services.
Course Outcomes:
1) Students will be able to explain the development of distributed Web applications, recalling the fundamental concepts related to the architecture of a distributed application.
2) Students will be able to examine the peculiar aspects of the client-server architecture, including the most used programming languages in this type of architecture.
3) Students will be able to categorize aspects related to the Grid architecture and Web services.
Artificial Intelligence and Knowledge Engineering
CEN3070
3 US Credits
The main objective of this course is to introduce the student to the most representative areas of Artificial Intelligence and to the modeling of complex problems about which any expert knowledge is had. On the one hand, Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the automatic resolution of problems. Within this scope, the main goals are to offer an alternative to classical optimization algorithms to find the solution to complex problems, and to check the potential of general-purpose computers in comparison with the intellectual capacity of humans. On the other hand, Knowledge Engineering is the set of methodologies designed to help capture and model knowledge within a certain domain for its exploitation by an automatic system. In this sense, in this subject you will learn to deal with complex problems in an analytical way and to use a set of tools and libraries that allows you to solve them. At the end of the course, the student must be able to model a problem efficiently and identify which techniques are the most appropriate for its resolution.
Course Outcomes:
1) Students will be able to evaluate the most representative areas of Artificial Intelligence and to the modeling of complex problems using expert knowledge.
2) Students will be able to assess the potential of general-purpose computers in comparison with the intellectual capacity of humans.
3) Students will be able to model a problem using artificial intelligence and distinguish which techniques are the most appropriate for its resolution.
Data Structures and Algorithm Analysis in C++
COP3530
3 US Credits
In this course students will learn how to design, write, and analyze the performance of C/C++ programs that handle structured data and perform more complex tasks, typical of larger software projects. Students should acquire skills in using generic principles for data representation & manipulation with a view for efficiency, maintainability, and code-reuse. At the end of the course, students will be able to demonstrate analytical comprehension of concepts such as abstract data types generic programming techniques, algorithms, and efficiency analysis.
Course Outcomes:
1) Students will be able to design, write, and analyze basic intuitive ideas about performance of C/C++ programs that handle structured data and perform more complex tasks, typical of larger software projects.
2) Students will be able to combine generic principles for data representation & manipulation with a view for efficiency, maintainability, and code-reuse.
3) Students will be able to manage analytical comprehension of concepts such as abstract data types, generic programming techniques, algorithms, and efficiency analysis.
Third year
7th semester
Algorithms and Complexity
COP2550
3 US Credits
The main objective of this course is to familiarize the student with the general techniques of algorithm design. In this course, the main algorithms and data structures that exist in the specific literature will be introduced. It will be a basis for later subjects where more modern and advanced techniques are studied in depth. Not only it is necessary for the student to know how to recognize effective algorithms, but also to know how to choose the most efficient algorithms for each situation. This implies knowing how to analyze and measure the complexity of an algorithm, knowing how to identify possible bottlenecks and prevent congestions that delay the execution of your program. To do this, the course will also provide how to determine the number of resources (temporary and memory) necessary to execute an algorithm, as well as to classify algorithms according to their computational complexity.
Course Outcomes:
1) Students will be able to employ general techniques of algorithm design, including the main algorithms and data structures that exist.
2) Students will be able to differentiate and distinguish the complexity family of an algorithm, identifying possible bottlenecks and prevent congestions that delay the execution of a program.
3) Students will be able to calculate the amount of resources (time and memory) necessary to execute an algorithm, as well as to classify algorithms according to their computational complexity.
Computer Structure
EEE3050
3 US Credits
This course is the continuation of the course on Computer Architecture and System Software. Its main objective is to address the evolution towards different computer architectures from the basic configuration of a computer, previously studied. The essential factor in this evolution will be the improvement of the performance in the configuration resulting from the application, mainly, on parallelism techniques. This course includes the following contents: functional organization, computer performance, interconnection, and communication systems, alternative and multiprocessing architectures. Based on this content, the specific competences of the subject that the student will acquire are deepen the hierarchies of memories, understand parallelism at the instruction level, understand how to use segmented instructions (pipelining), understand parallelism at the level of data, understand the shared memory systems, identify and understand the operation of different interconnection systems.
Course Outcomes:
1) Students will be able to inspect the evolution towards different computer architectures from the basic configuration of a computer.
2) Students will be able to evaluate parallelism at the instruction level, propose Chow to use segmented instructions (pipelining), revise parallelism at the level of data and the shared memory systems, compare the operation of different interconnection systems.
Networks and the Internet
EEL3123
3 US Credits
This class wishes to introduce web calculators, and more generally, telecommunication web services. It will offer all the principal concepts on data transmission, through wireless and guided services. It will also describe the characteristics of those main systems which are used in geographical areas (telephone line, mobile networks), in metropolitan areas (WiMAX), and locally (Ethernet, Wi-Fi,), explaining their protocols and their structures. Lastly, it will describe the functioning, the protocols, and the applications of the Internet.
Course Outcomes:
1) Students will be able to analyze web calculators, and more generally, telecommunication web services, evaluating the principal concepts on data transmission, through wireless and guided services.
2) Students will be able to compare the characteristics of those main systems which are used in geographical areas (telephone line, mobile networks), in metropolitan areas (WiMAX), and locally (Ethernet, Wi-Fi,), explaining their protocols and their structures.
8th semester
Neural Networks and Fuzzy Logic
EEE3032
3 US Credits
The principal objective of this subject is to introduce students to neural networks and fuzzy theory from an engineering perspective. In the identification and control of dynamic systems, neural networks and fuzzy systems can be implemented as model-free estimators and/or controllers. As trainable dynamic systems, these intelligent control systems can learn from experience with numerical and linguistic sample data.
Course Outcomes:
1) Students will be able to revise neural networks and fuzzy theory from an engineering perspective.
2) Students will be able to formulate identification and control schemes for dynamic systems, as model-free estimators and/or controllers. As trainable dynamic systems, these intelligent control systems can learn from experience with numerical and linguistic sample data.
Information Retrieval
COP2410
3 US Credits
The principal objective of this subject is to present the tecniques which are used to automatically back up information from heterogeneous and distributed sources. It will offer various competences in the comprehension of processes, and in information processing techniques, which are those tools that characterize modern applications, and modern web search engines.
Particular focus will be put on computer technologies, and automatic-learning technologies, which allow a fast development of systems based on reusing both available knowledge and data, in an electronic format, in open sources. All of this will be discussed and analyzed in relation to modern applications on Web sources and sites.
Course Outcomes:
1) Students will be able to recognize all those system technologies which are used to automatically back up information from heterogeneous and distributed sources.
2) Students will be able to use the comprehension of processes, and in information processing techniques, which are those tools that characterize modern applications, and modern web search engines.
3) Students will be able to practice fast development of systems based on reusing both available knowledge and data, in an electronic format, in open sources.
Embedded Software Engineering
COP4301
3 US Credits
The presence of embedded software, which was initially limited to aircrafts, is gaining popularity also for land transportation, particularly with automobiles, where there is a wide growth, also for the increasing number of services, the necessity of facilitating variations, the tighter requisites of reliability, and safety. This class tackles the extensive subject of software development processes, inside mobiles, with a particular concern for automobiles, the material of engineering methods, of necessary software to convey the notion of the embedded software as an economic and quality one, which is effective, correct, and reusable. It must be reliable, considering that today 30% of severe malfunctioning comes from software deficiency.
Course Outcomes: 1) Students will be able to assemble software development processes, inside mobiles, with a particular concern for automobiles, the material of engineering methods, of necessary software. 2) Students will be able to revise the notion of the embedded software as an economic and quality one, which is effective, correct, and reusable. It must be reliable, considering that today 30% of severe malfunctioning comes from software deficiency.
Project Management
CEN3880
3 US Credits
The main objective of this course is to know the most appropriate methodology for the successful execution of projects and to reinforce those areas of knowledge that their managers must face every day. A basic issue to be resolved, is the following: the projects are delivered within the required time frame, with the budgeted cost and with the agreed quality, otherwise, on the contrary, the delays and cost overrun the projects damaging the relationship with the clients and profitability of the business. The answer to these questions is to ensure that the company is capable of successfully undertaking the temporary, collective, and singular effort that the nature of the projects requires. The company can no longer be seen as the sum of functional groups that, although they work as a team, lend themselves to isolating themselves in their own departmental objectives. Project management must appear as a union, a harmonious set, of competencies and abilities to act as a driving force and integrator of the organization’s capacities to put them at the service of the project objectives and thus be able to obtain the success of the projects. Nowadays, the success of a project, based on the fulfillment of its requirements, in the foreseen term, without exceeding the budgeted costs and with the defined quality, is an objective that no longer depends exclusively on a good estimation, planning and control. Hence, it is no longer sufficient to understand project management simply as a technical function dedicated to planning and controlling the development of projects individually. The key to overcoming these challenges is the establishment of a correct strategy, reflected in a correct selection of projects and, at the head of them, the most suitable people. To the extent that the execution of this project portfolio is successful, it will be to the extent that the success of the company and its long-term survival will be ensured. These fundamental questions will be analyzed throughout this course.
Course Outcomes:
1) Students will be able to manage the most appropriate methodology for the successful execution of projects and to reinforce those areas of knowledge that their managers must face every day.
2) Students will be able to appraise Project management as a union, a harmonious set, of competencies and abilities to act as a driving force and integrator of the organization’s capacities to put them at the service of the project objectives and thus be able to obtain the success of the projects.
3) Students will be able to propose a correct strategy, reflected in a correct selection of projects and, at the head of them, the most suitable people.
9th semester
Advanced Computer Programming
COP3500
3 US Credits
This course is aimed to study advanced computer programming technologies, apply advanced programming to data technologies, and study the concept of Object Distribution and invoking its services remotely in Distributed environment. Also, study algorithmic examples in distributed, concurrent, and parallel environments. At the end of this course the student will be able to: solve problems using advanced programming, problems for multi-core or distributed, and work with concurrent/Parallel environments.
Course Outcomes:
1) Students will be able to apply advanced programming to data technologies and use the concept of Object Distribution and invoking its services remotely in Distributed environment.
2) Students will be able to solve problems using advanced programming, problems for multi-core or distributed, and work with concurrent/Parallel environments.
Information and Encoding
COP3501
3 US Credits
The class has the main objective of offering to the students the ability of dealing with digital signals, which must be either memorized or transmitted on a support, to reduce redundancy, and increasing possibilities of a correct information rescue, after the memorization/transmission.
Course Outcomes:
1) Students will be able to combine digital signals, which must be either memorized or transmitted on a support.
2) Students will be able to design systems to reduce redundancy, and increasing possibilities of a correct information rescue, after the memorization/transmission.
Installations and Systems Performance and Quality
COP3601
3 US Credits
Defining and describing systems, networks, and computer systems. Characterizing their qualities, their performances, and metric. It will also present methods for building models. Students will use these models for planning and upgrade the quality of the service requested.
Course Outcomes:
1) Students will be able to differentiate and examine systems, networks, and computer systems, characterizing their qualities, their performances, and metric.
2) Students will be able to propose models for planning and upgrade the quality of the service requested.
Fourth year
10th semester
Online Information System for Business
COP3701
3 US Credits
Business intelligence systems are applications and technologies for gathering, storing, analyzing, and accessing information for better business decision-making. Examples of BI systems include measuring and monitoring key performance indicators, benchmarking and forecasting sales, performing data mining and analysis of customer information to discover new business opportunities, and building enterprise dashboards to integrate and visualize information from various business areas. The demand for building and managing BI systems in today’s very competitive and challenging economy is high. This course guides students through the complete life cycle of building and managing BI and analytics systems. Students are introduced step by step to the various phases and complexities in building and supporting successful BI and analytics systems. Topics covered include best practices in BI requirement gathering; BI project management; data warehousing; ETL (extract, transform, and load); data mining, predictive analytics, online analytical processing, BI application development, BI implementation, and production support.
Course Outcomes:
1) Students will be able to examine the complete life cycle of building and managing BI and analytics systems, including gathering, storing, analyzing, and accessing information for better business decision-making.
2) Students will be able to manage the various phases and complexities in building and supporting successful BI and analytics systems, including best practices in BI requirement gathering; BI project management; data warehousing; ETL (extract, transform, and load); data mining, predictive analytics, online analytical processing, BI application development, BI implementation, and production support.
Intelligent Web System
COP3801
3 US Credits
Introducing in an historical context the concept of “intelligence”, when associated to systems/agents, analyzing the methodologies developed for the analysis of complex issues, evaluating the complexity of single approaches, identifying the structures and the strategies for the resolution of more complex problems. Lastly, it will analyze the specificity of the problematic, in the moment in which web intelligent agents are created.
Course Outcomes:
1) Students will be able to value the concept of “intelligence”, when associated to systems/agents, analyzing the methodologies developed for the analysis of complex issues, evaluating the complexity of single approaches, identifying the structures and the strategies for the resolution of more complex problems.
2) Students will be able to analyze the problems specificity, in the moment in which web intelligent agents are created.
Software Engineering and Quality
CEN2020
3 US Credits
Defining the software industrial production process, formalizing the life cycle of the software product, from the requisites phase to the phase of realization and integration, following the most modern methodologies, which are oriented towards objects, also introducing methodologies of verifying the software quality, testing methods, and planning time sheets.
Course Outcomes:
1) Students will be able to employ the software industrial production process, formalizing the life cycle of the software product, from the requisites phase to the phase of realization and integration.
2) Students will be able to experiment the most modern methodologies, which are object oriented, also introducing methodologies for verifying the software quality, testing methods, and planning time sheets.
11th semester
Wireless Network and System
CNT4704
3 US Credits
The class will Introduce wireless systems and networks, including mobile networks. It wishes to offer all those necessary elements to design a radio system. It wants to discuss the main quality parameters, also evaluating their performances. It will discuss the characterization of both protocols and structures of GSM and UMTS systems, and of those new wireless systems.
Course Outcomes:
1) Students will be able to design a radio system using wireless systems and networks, including mobile networks.
2) Students will be able to value the characterization of protocols and structures for GSM and UMTS systems, and of those new wireless systems.
Advanced Algorithm Design
CEN3180
3 US Credits
The main objective of this course is to deepen into the techniques of algorithm design, or problem-solving techniques, and it will focus accurately on how to verify if a program meets your specifications. These techniques can be applied to a multitude of problems of all kinds. The profound change that it has brought about in our style of life, not only in computing and information processing, the algorithms on which Google is based, is enough to get an idea of the fundamental importance of a subject like this. It will be not focused on a specific programming language, although the possibility of implementing an algorithm in an application that can be executed on a computer is essential to understand the operation and efficiency of the algorithms that will be studied. It must be considered that the technology of our computers is apparently exponentially advancing, but at the same time the amount of data is required, no, that is needed to process at the same time grows at an ever-greater rate. Therefore, the efficiency will also be dealt with, a fundamental concept when it comes to judging the goodness of algorithms. Obviously, an algorithm is asked to solve a given problem, but it is also asked to do so with the appropriate resources that is had or that can be reasonably had.
Course Outcomes:
1) Students will be able to select the advanced techniques of algorithm design, or problem-solving techniques.
2) Students will be able to interpret if a program truly meets the specifications.
Simulation Methods and Languages
COP4400
3 US Credits
Defining the finalities, and the characteristics of a simulative approach to system studying, presenting different methods for the construction of their own simulation models. Using planning models, and adjusting systems, and networks.
Course Outcomes:
1) Students will be able to evaluate the finalities, and the characteristics of a simulative approach to system studying, presenting different methods for the construction of their own simulation models.
2) Students will be able to design planning models, and tunning systems, and networks for simulations.
12th semester
Computer Engineering Capstone Project
CIS4011
6 US Credits
A capstone course in which the student applies computer engineering concepts and skills to a computer-engineering project. Team projects are strongly encouraged. Projects will cover all aspects of the computer life cycle: specification of requirements and functionality; project planning and scoping; system and user interface definition; analysis of architectural solutions; detailed system design; implementation and integration; testing and quality assurance; reliability, usability, and performance testing, documentation, evolution, and change management.
Prerequisite(s): Students are required to complete all other program credits before registering for the capstone project course.
Course Outcomes:
1) Students will be able to apply computer engineering concepts and skills to a computer-engineering project.
2) Students will be able to formulate specification of requirements and functionality; project planning and scoping; system and user interface definition; analysis of architectural solutions; detailed system design; implementation and integration; testing and quality assurance; reliability, usability, and performance testing, documentation, evolution, and change management.
Why study at MIU?
Earning your Bachelor’s Degree in Computer Science at MIU will accelerate your professional career, preparing you for today’s business world. If you take this degree program with us, you can enjoy:
- A U.S. degree adapted to the needs of the American global market.
- Access to quality networking that connects you with students from all over the world, broadening your horizons and your opportunities.
- Flexible methodology that includes onboarding, personal advising, live and recorded classes, 24/7 technical support, and access to all the online resources.
- Affordable prices and a simple enrollment process for easy access to a high-quality education.

Keep learning: add a specialization
Deepen your knowledge and stand out from the competition with our Continuing Education Certificate programs.
Cybersecurity
Develop a strategic vision to implement effective digital protection protocols.
Data Science
Master the techniques of data mining and data processing.
Digital Project Management
Master the tools and methodologies to lead multidisciplinary teams and manage complex projects.
Data & Business Analytics
Make decisions based on strategic data analysis.
Strategic Management and Organizational Leadership
Learn how to lead teams and navigate crises effectively.
Emotional Intelligence and Positive Discipline
Support your students’ talents and help them grow.
Design Management
Lead creative projects with successful brand communication strategies.
Corporate Finance
Optimize your company's financial management to gain a competitive edge.
Digital Marketing 360º
Learn effective strategies to connect with your audience and grow your business.
E-commerce and Digital Business Management
Explore the latest trends and find new business opportunities in e-commerce.
Skills for Lawyers
Adapt to the ever-changing demands of the legal profession.
Legal Tech
Become a sought-after legal expert in the digital marketplace.
Quality and Patient Safety
Become a healthcare professional capable of managing risks and crisis situations.
Student profile
MIU’s Bachelor’s Degree in Computer Science is designed for students looking to develop their professional career with specialized knowledge in areas such as programming, systems design, cybersecurity, and computer networks.
This degree provides you with theoretical and practical knowledge in artificial intelligence, software engineering, hardware design, system architecture, and data security, which form the basis of modern computer systems.
You will learn everything from how a computer works to how to use various programming tools and techniques, becoming a sought-after professional for companies in any economic sector.
In four years, you will gain the knowledge you need to work in one of the most in-demand industries.
Testimonials



Requirements
To apply for this online program, you must submit the following:
- High school diploma or GED.
- Copy of your passport or official ID.
- Completed application form.
- Updated resume.
- If you are not a U.S. resident or English is not your native language, please check the additional requirements.

Key dates
- Fall semester: September – December
- Enrollment: August
- Spring semester: January – May
- Enrollment: December
- Summer semester: May – August
- Enrollment: April

A leader in online education
We are proud to be part of PROEDUCA Universidades, an educational group at the forefront of online learning at the international level. This allows us to offer you a high-quality U.S. education at a competitive and affordable price.
MIU City University Miami is accredited by the Distance Education Accrediting Commission (DEAC) licensed by the Florida Commission for Independent Education of the Florida Department of Education.
COUNTRIES
STUDENTS
YEARS OF EXPERIENCE

MIU City University Miami is accredited by the Distance Education Accrediting Commission (DEAC) licensed by the Florida Commission for Independent Education of the Florida Department of Education.



>
Request information
$14,400*
$120 USD credit